Chapter 12: Properties of Stars
Chapter 1
How Science Works
- The Scientific Method
- Evidence
- Measurements
- Units and the Metric System
- Measurement Errors
- Estimation
- Dimensions
- Mass, Length, and Time
- Observations and Uncertainty
- Precision and Significant Figures
- Errors and Statistics
- Scientific Notation
- Ways of Representing Data
- Logic
- Mathematics
- Geometry
- Algebra
- Logarithms
- Testing a Hypothesis
- Case Study of Life on Mars
- Theories
- Systems of Knowledge
- The Culture of Science
- Computer Simulations
- Modern Scientific Research
- The Scope of Astronomy
- Astronomy as a Science
- A Scale Model of Space
- A Scale Model of Time
- Questions
Chapter 2
Early Astronomy
- The Night Sky
- Motions in the Sky
- Navigation
- Constellations and Seasons
- Cause of the Seasons
- The Magnitude System
- Angular Size and Linear Size
- Phases of the Moon
- Eclipses
- Auroras
- Dividing Time
- Solar and Lunar Calendars
- History of Astronomy
- Stonehenge
- Ancient Observatories
- Counting and Measurement
- Astrology
- Greek Astronomy
- Aristotle and Geocentric Cosmology
- Aristarchus and Heliocentric Cosmology
- The Dark Ages
- Arab Astronomy
- Indian Astronomy
- Chinese Astronomy
- Mayan Astronomy
- Questions
Chapter 3
The Copernican Revolution
- Ptolemy and the Geocentric Model
- The Renaissance
- Copernicus and the Heliocentric Model
- Tycho Brahe
- Johannes Kepler
- Elliptical Orbits
- Kepler's Laws
- Galileo Galilei
- The Trial of Galileo
- Isaac Newton
- Newton's Law of Gravity
- The Plurality of Worlds
- The Birth of Modern Science
- Layout of the Solar System
- Scale of the Solar System
- The Idea of Space Exploration
- Orbits
- History of Space Exploration
- Moon Landings
- International Space Station
- Manned versus Robotic Missions
- Commercial Space Flight
- Future of Space Exploration
- Living in Space
- Moon, Mars, and Beyond
- Societies in Space
- Questions
Chapter 4
Matter and Energy in the Universe
- Matter and Energy
- Rutherford and Atomic Structure
- Early Greek Physics
- Dalton and Atoms
- The Periodic Table
- Structure of the Atom
- Energy
- Heat and Temperature
- Potential and Kinetic Energy
- Conservation of Energy
- Velocity of Gas Particles
- States of Matter
- Thermodynamics
- Entropy
- Laws of Thermodynamics
- Heat Transfer
- Thermal Radiation
- Wien's Law
- Radiation from Planets and Stars
- Internal Heat in Planets and Stars
- Periodic Processes
- Random Processes
- Questions
Chapter 5
The Earth-Moon System
- Earth and Moon
- Early Estimates of Earth's Age
- How the Earth Cooled
- Ages Using Radioactivity
- Radioactive Half-Life
- Ages of the Earth and Moon
- Geological Activity
- Internal Structure of the Earth and Moon
- Basic Rock Types
- Layers of the Earth and Moon
- Origin of Water on Earth
- The Evolving Earth
- Plate Tectonics
- Volcanoes
- Geological Processes
- Impact Craters
- The Geological Timescale
- Mass Extinctions
- Evolution and the Cosmic Environment
- Earth's Atmosphere and Oceans
- Weather Circulation
- Environmental Change on Earth
- The Earth-Moon System
- Geological History of the Moon
- Tidal Forces
- Effects of Tidal Forces
- Historical Studies of the Moon
- Lunar Surface
- Ice on the Moon
- Origin of the Moon
- Humans on the Moon
- Questions
Chapter 6
The Terrestrial Planets
- Studying Other Planets
- The Planets
- The Terrestrial Planets
- Mercury
- Mercury's Orbit
- Mercury's Surface
- Venus
- Volcanism on Venus
- Venus and the Greenhouse Effect
- Tectonics on Venus
- Exploring Venus
- Mars in Myth and Legend
- Early Studies of Mars
- Mars Close-Up
- Modern Views of Mars
- Missions to Mars
- Geology of Mars
- Water on Mars
- Polar Caps of Mars
- Climate Change on Mars
- Terraforming Mars
- Life on Mars
- The Moons of Mars
- Martian Meteorites
- Comparative Planetology
- Incidence of Craters
- Counting Craters
- Counting Statistics
- Internal Heat and Geological Activity
- Magnetic Fields of the Terrestrial Planets
- Mountains and Rifts
- Radar Studies of Planetary Surfaces
- Laser Ranging and Altimetry
- Gravity and Atmospheres
- Normal Atmospheric Composition
- The Significance of Oxygen
- Questions
Chapter 7
The Giant Planets and Their Moons
- The Gas Giant Planets
- Atmospheres of the Gas Giant Planets
- Clouds and Weather on Gas Giant Planets
- Internal Structure of the Gas Giant Planets
- Thermal Radiation from Gas Giant Planets
- Life on Gas Giant Planets?
- Why Giant Planets are Giant
- Gas Laws
- Ring Systems of the Giant Planets
- Structure Within Ring Systems
- The Origin of Ring Particles
- The Roche Limit
- Resonance and Harmonics
- Tidal Forces in the Solar System
- Moons of Gas Giant Planets
- Geology of Large Moons
- The Voyager Missions
- Jupiter
- Jupiter's Galilean Moons
- Jupiter's Ganymede
- Jupiter's Europa
- Jupiter's Callisto
- Jupiter's Io
- Volcanoes on Io
- Saturn
- Cassini Mission to Saturn
- Saturn's Titan
- Saturn's Enceladus
- Discovery of Uranus and Neptune
- Uranus
- Uranus' Miranda
- Neptune
- Neptune's Triton
- Pluto
- The Discovery of Pluto
- Pluto as a Dwarf Planet
- Dwarf Planets
- Questions
Chapter 8
Interplanetary Bodies
- Interplanetary Bodies
- Comets
- Early Observations of Comets
- Structure of the Comet Nucleus
- Comet Chemistry
- Oort Cloud and Kuiper Belt
- Kuiper Belt
- Comet Orbits
- Life Story of Comets
- The Largest Kuiper Belt Objects
- Meteors and Meteor Showers
- Gravitational Perturbations
- Asteroids
- Surveys for Earth Crossing Asteroids
- Asteroid Shapes
- Composition of Asteroids
- Introduction to Meteorites
- Origin of Meteorites
- Types of Meteorites
- The Tunguska Event
- The Threat from Space
- Probability and Impacts
- Impact on Jupiter
- Interplanetary Opportunity
- Questions
Chapter 9
Planet Formation and Exoplanets
- Formation of the Solar System
- Early History of the Solar System
- Conservation of Angular Momentum
- Angular Momentum in a Collapsing Cloud
- Helmholtz Contraction
- Safronov and Planet Formation
- Collapse of the Solar Nebula
- Why the Solar System Collapsed
- From Planetesimals to Planets
- Accretion and Solar System Bodies
- Differentiation
- Planetary Magnetic Fields
- The Origin of Satellites
- Solar System Debris and Formation
- Gradual Evolution and a Few Catastrophies
- Chaos and Determinism
- Extrasolar Planets
- Discoveries of Exoplanets
- Doppler Detection of Exoplanets
- Transit Detection of Exoplanets
- The Kepler Mission
- Direct Detection of Exoplanets
- Properties of Exoplanets
- Implications of Exoplanet Surveys
- Future Detection of Exoplanets
- Questions
Chapter 10
Detecting Radiation from Space
- Observing the Universe
- Radiation and the Universe
- The Nature of Light
- The Electromagnetic Spectrum
- Properties of Waves
- Waves and Particles
- How Radiation Travels
- Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation
- The Doppler Effect
- Invisible Radiation
- Thermal Spectra
- The Quantum Theory
- The Uncertainty Principle
- Spectral Lines
- Emission Lines and Bands
- Absorption and Emission Spectra
- Kirchoff's Laws
- Astronomical Detection of Radiation
- The Telescope
- Optical Telescopes
- Optical Detectors
- Adaptive Optics
- Image Processing
- Digital Information
- Radio Telescopes
- Telescopes in Space
- Hubble Space Telescope
- Interferometry
- Collecting Area and Resolution
- Frontier Observatories
- Questions
Chapter 11
Our Sun: The Nearest Star
- The Sun
- The Nearest Star
- Properties of the Sun
- Kelvin and the Sun's Age
- The Sun's Composition
- Energy From Atomic Nuclei
- Mass-Energy Conversion
- Examples of Mass-Energy Conversion
- Energy From Nuclear Fission
- Energy From Nuclear Fusion
- Nuclear Reactions in the Sun
- The Sun's Interior
- Energy Flow in the Sun
- Collisions and Opacity
- Solar Neutrinos
- Solar Oscillations
- The Sun's Atmosphere
- Solar Chromosphere and Corona
- Sunspots
- The Solar Cycle
- The Solar Wind
- Effects of the Sun on the Earth
- Cosmic Energy Sources
- Questions
Chapter 13
Star Birth and Death
- Star Birth and Death
- Understanding Star Birth and Death
- Cosmic Abundance of Elements
- Star Formation
- Molecular Clouds
- Young Stars
- T Tauri Stars
- Mass Limits for Stars
- Brown Dwarfs
- Young Star Clusters
- Cauldron of the Elements
- Main Sequence Stars
- Nuclear Reactions in Main Sequence Stars
- Main Sequence Lifetimes
- Evolved Stars
- Cycles of Star Life and Death
- The Creation of Heavy Elements
- Red Giants
- Horizontal Branch and Asymptotic Giant Branch Stars
- Variable Stars
- Magnetic Stars
- Stellar Mass Loss
- White Dwarfs
- Supernovae
- Seeing the Death of a Star
- Supernova 1987A
- Neutron Stars and Pulsars
- Special Theory of Relativity
- General Theory of Relativity
- Black Holes
- Properties of Black Holes
- Questions
Chapter 14
The Milky Way
- The Distribution of Stars in Space
- Stellar Companions
- Binary Star Systems
- Binary and Multiple Stars
- Mass Transfer in Binaries
- Binaries and Stellar Mass
- Nova and Supernova
- Exotic Binary Systems
- Gamma Ray Bursts
- How Multiple Stars Form
- Environments of Stars
- The Interstellar Medium
- Effects of Interstellar Material on Starlight
- Structure of the Interstellar Medium
- Dust Extinction and Reddening
- Groups of Stars
- Open Star Clusters
- Globular Star Clusters
- Distances to Groups of Stars
- Ages of Groups of Stars
- Layout of the Milky Way
- William Herschel
- Isotropy and Anisotropy
- Mapping the Milky Way
- Questions
Chapter 15
Galaxies
- The Milky Way Galaxy
- Mapping the Galaxy Disk
- Spiral Structure in Galaxies
- Mass of the Milky Way
- Dark Matter in the Milky Way
- Galaxy Mass
- The Galactic Center
- Black Hole in the Galactic Center
- Stellar Populations
- Formation of the Milky Way
- Galaxies
- The Shapley-Curtis Debate
- Edwin Hubble
- Distances to Galaxies
- Classifying Galaxies
- Spiral Galaxies
- Elliptical Galaxies
- Lenticular Galaxies
- Dwarf and Irregular Galaxies
- Overview of Galaxy Structures
- The Local Group
- Light Travel Time
- Galaxy Size and Luminosity
- Mass to Light Ratios
- Dark Matter in Galaxies
- Gravity of Many Bodies
- Galaxy Evolution
- Galaxy Interactions
- Galaxy Formation
- Questions
Chapter 16
The Expanding Universe
- Galaxy Redshifts
- The Expanding Universe
- Cosmological Redshifts
- The Hubble Relation
- Relating Redshift and Distance
- Galaxy Distance Indicators
- Size and Age of the Universe
- The Hubble Constant
- Large Scale Structure
- Galaxy Clustering
- Clusters of Galaxies
- Overview of Large Scale Structure
- Dark Matter on the Largest Scales
- The Most Distant Galaxies
- Black Holes in Nearby Galaxies
- Active Galaxies
- Radio Galaxies
- The Discovery of Quasars
- Quasars
- Types of Gravitational Lensing
- Properties of Quasars
- The Quasar Power Source
- Quasars as Probes of the Universe
- Star Formation History of the Universe
- Expansion History of the Universe
- Questions
Chapter 17
Cosmology
- Cosmology
- Early Cosmologies
- Relativity and Cosmology
- The Big Bang Model
- The Cosmological Principle
- Universal Expansion
- Cosmic Nucleosynthesis
- Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
- Discovery of the Microwave Background Radiation
- Measuring Space Curvature
- Cosmic Evolution
- Evolution of Structure
- Mean Cosmic Density
- Critical Density
- Dark Matter and Dark Energy
- Age of the Universe
- Precision Cosmology
- The Future of the Contents of the Universe
- Fate of the Universe
- Alternatives to the Big Bang Model
- Space-Time
- Particles and Radiation
- The Very Early Universe
- Mass and Energy in the Early Universe
- Matter and Antimatter
- The Forces of Nature
- Fine-Tuning in Cosmology
- The Anthropic Principle in Cosmology
- String Theory and Cosmology
- The Multiverse
- The Limits of Knowledge
- Questions
Chapter 18
Life On Earth
- Nature of Life
- Chemistry of Life
- Molecules of Life
- The Origin of Life on Earth
- Origin of Complex Molecules
- Miller-Urey Experiment
- Pre-RNA World
- RNA World
- From Molecules to Cells
- Metabolism
- Anaerobes
- Extremophiles
- Thermophiles
- Psychrophiles
- Xerophiles
- Halophiles
- Barophiles
- Acidophiles
- Alkaliphiles
- Radiation Resistant Biology
- Importance of Water for Life
- Hydrothermal Systems
- Silicon Versus Carbon
- DNA and Heredity
- Life as Digital Information
- Synthetic Biology
- Life in a Computer
- Natural Selection
- Tree Of Life
- Evolution and Intelligence
- Culture and Technology
- The Gaia Hypothesis
- Life and the Cosmic Environment
Chapter 19
Life in the Universe
- Life in the Universe
- Astrobiology
- Life Beyond Earth
- Sites for Life
- Complex Molecules in Space
- Life in the Solar System
- Lowell and Canals on Mars
- Implications of Life on Mars
- Extreme Environments in the Solar System
- Rare Earth Hypothesis
- Are We Alone?
- Unidentified Flying Objects or UFOs
- The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence
- The Drake Equation
- The History of SETI
- Recent SETI Projects
- Recognizing a Message
- The Best Way to Communicate
- The Fermi Question
- The Anthropic Principle
- Where Are They?
Stars of Different Sizes
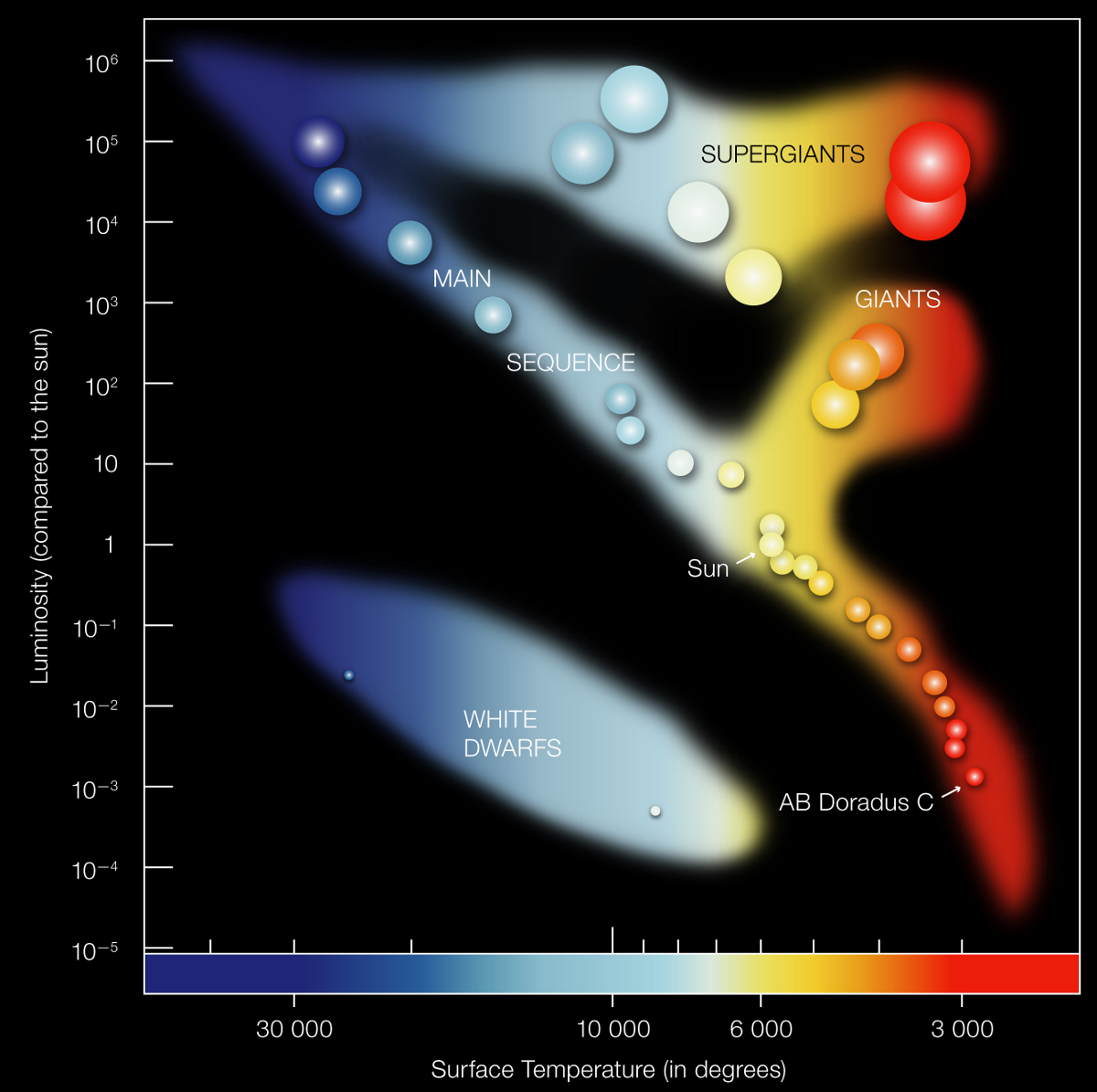
As astronomers studied the properties of large samples of stars, they found stars with many different combinations of luminosity and temperature. Most of these stars had properties that placed them at different positions on the main sequence of the H-R diagram, slanting from high luminosity and high temperature to low luminosity and low temperature. However, some stars had properties dissimilar from any main sequence star.
Some red stars with spectral types K and M have much higher luminosity than the faint, main-sequence K and M stars. They radiate more light than the fainter stars of the same temperature. According to the Stefan-Boltzmann law, they must have larger areas. Hertzsprung named them giant stars. Most are called red giants since their outer regions are cool and thus look reddish.

Other stars are brighter than the giants or the main-sequence O stars. Application of the Stefan-Boltzmann law showed that they were larger than giant; they came to be called supergiant stars. For example, the enormous red giant Antares, in the constellation Scorpius, would dwarf the Sun. Antares is only ten times the mass of the Sun but it is so bloated it is almost 900 times the size; the Sun would fit into Antares 700 million times over!
Yet other stars have combinations of high temperature and low luminosity that place them below the main sequence of the H-R diagram. By using the same radiation law to derive their sizes, astronomers recognized that these dim stars were unusually small. They came to be called white dwarf stars. A white dwarf the mass of the Sun would be a hundred times smaller than the Sun, so a million white dwarfs would fit inside the Sun. Combining the last two comparisons, a thousand trillion white dwarfs would fit inside a red supergiant! The size range of stars is enormous.

Hertzsprung, Russell, and their followers showed the systematic properties of different types of stars: one type was the main sequence; the giants, supergiants, and white dwarfs were distinctly different types of stars. These types refer to the luminosity class of a star. The main sequence — seen as stars whose properties place them on a diagonal of the H-R diagram — is the set of stars converting hydrogen into helium, a set that includes the Sun. Half of the most prominent stars in the sky are giants or supergiants. Although the whales among the fishes are rare, they account for many of the familiar stars. Their combinations of size and luminosity mean they must have a different mechanism for energy production than the Sun and other main sequence stars. Further work showed that these groups occur all over the sky and at many distances from the Sun. This meant that universal physical processes could be sought to explain the different non-main-sequence stars.
Occasionally astronomers find groups of stars at about the same distance from us and formed at about the same time. These star clusters offer, so to speak, living H-R diagrams in the sky. Just by studying the colors and brightness of stars in a cluster, astronomers can see the pattern of the H-R diagram. Most of the stars are on the main sequence; the brightest ones are blue-white, and the faintest ones are red.
The H-R diagram only shows temperature and luminosity. However, we can use the Stefan-Boltzmann law to calculate stellar radius and show it on the H-R diagram as well. The important concept is this: any point on the H-R diagram corresponds to a star of a certain radius. The reasoning should be familiar. Any point on the diagram corresponds to a certain temperature T. According to the Stefan-Boltzmann law, any surface at temperature T must radiate a certain amount of energy per square meter each second. But any point on the diagram also corresponds to a particular luminosity L, which is the total amount of energy radiated each second. This luminosity fixes the number of square meters involved; giving us the total area and thus the radius.

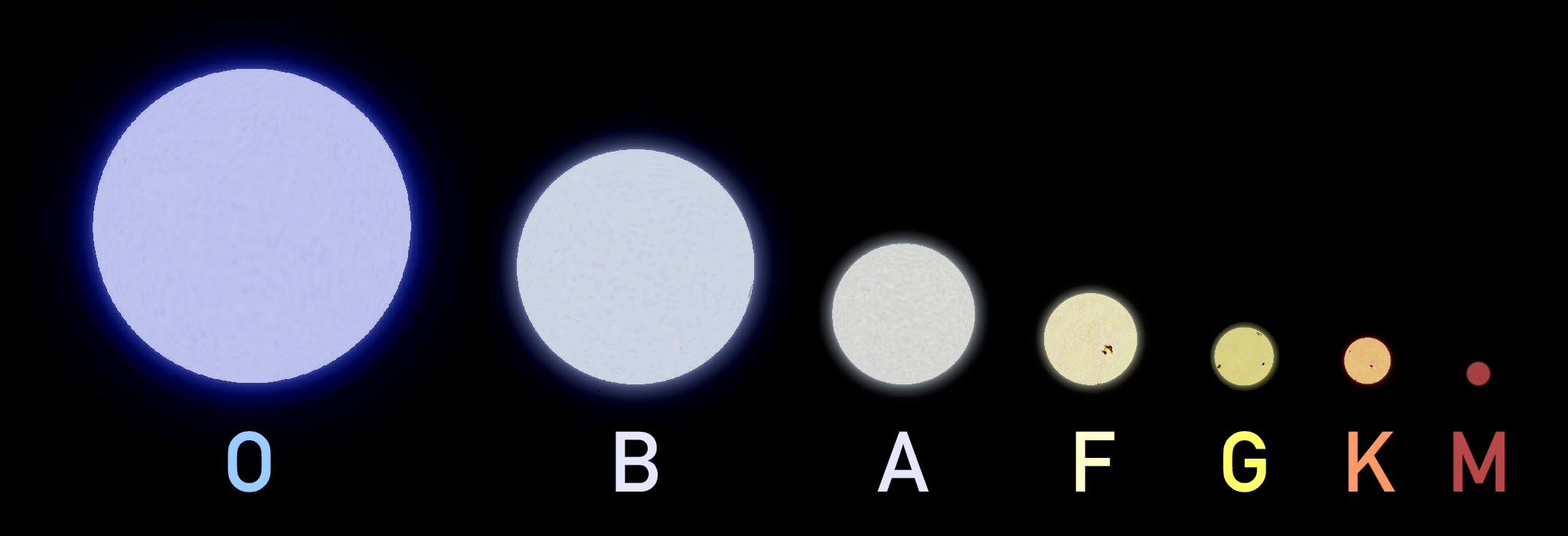
There is an enormous range in the physical properties of stars in the H-R diagram. Astronomers have the practical problem that stars with the same color might be quite different in their other properties. To see this, consider stars of different luminosity that have the same surface temperature (stars aligned vertically in the H-R diagram). Arcturus is over ten times larger than the Sun but has the same color. Betelgeuse is more than 10,000 times larger than Proxima Centauri but they both have a reddish color. Without knowing distances, is there any way to distinguish main sequence stars, giants, and supergiants of the same color? Yes. The more diffuse atmosphere in the larger stars gives fewer atomic collisions and a narrower absorption line. Spectroscopy can be sufficient to establish the luminosity class (main sequence, giant, supergiant) of a star. This allows a distance to be estimated, even if no parallax measurement is possible. However, spectral diagnostics apply to the outer layers of a star so they are indirect; the main differences between these star types stem from their masses and their energy production mechanisms.

